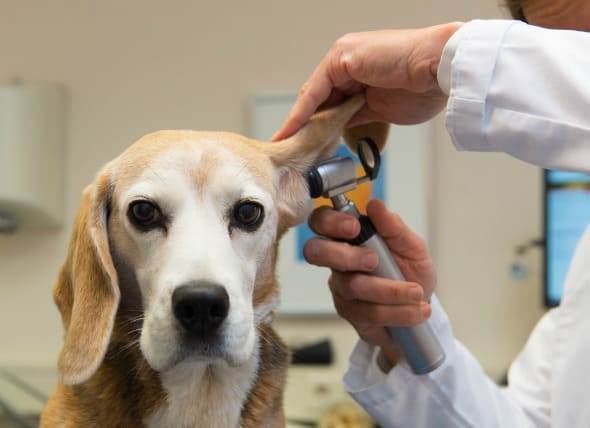
Fractures in companion pets is often a traumatic experience for both you and your pet, and there are a few things you should know to help both of you make the best of a bad situation!
First, it’s quite likely that your veterinarian will recommend surgical stabilization of the fracture. Cats and dogs and cats with fractures are treated surgically more often than are humans. There are two primary reasons for this:
- Compared to humans, animals more commonly fracture the major bones closest to the body, the femur in the hind limb and the humerus in the front limb. (Fractures in these bones are often due to major traumas in our pets, such as automobile accidents.) Fractures of the femur and humerus do not lend themselves to stabilization with splints or casts.
- Placing and maintaining casts or splints are major challenges in dogs and cats. Keeping casts clean and dry, and avoiding pressure sores under the bandage material, can be nearly impossible in active pets. In addition, in very small animals, the weight of a cast or splint may make it difficult to impossible for the animal to move around.
Surgery
If surgery is recommended, it will involve the application of various metal surgical implants such as pins, wires, plates, or screws. The primary goal of fracture fixation surgeries is to restore broken bones to their original anatomic position and rigidly fix them in place while healing occurs.
Post-Operative Care
After surgery, it will be your job as the owner to follow the post-operative care instructions very closely. While most animals will be encouraged to use the surgically-repaired limb, this activity must be under strict control. Surgical implants are strong but neither the implants nor the healing bone can withstand high energy or high impact movements.
Keeping the animal from licking at the surgical incision is imperative, at least until the sutures are removed. Persistent licking at a surgical wound will delay healing and is the major cause of incision infections.
Pain Control
How do you know if your pet is painful after surgery? Obviously, some discomfort is to be expected after the trauma of the injury and subsequent surgery. Your veterinarian will provide pain relief, especially during the in-hospital period. After your pet comes home, you should watch for signs of pain by observing whether your pet is able to settle down, rest, and sleep.
Animals in chronic pain have difficulty getting comfortable and will be reluctant to sleep for normal periods. You should also watch the limb for signs of swelling, redness, or discharge at the surgery site. The pet’s appetite and changes in the use of the limb are also critical signs to monitor. A patient who has been bearing some weight on the leg and suddenly stops doing so, or has a sudden decrease in appetite, should be reported to your veterinarian.
The following are a few common surgically-repaired fractures in small animals.
Humeral Condylar Fractures
Fractures involving the very end of the humerus, at the elbow joint, are common in puppies, especially between 4 to 6 months of age. These are most common in spaniel breeds, but can occur in many other types of dogs. Most occur due to “impact injuries” (e.g., puppy jumped off a high place or fell from the owner’s arms). Surgery is necessary to reestablish normal elbow function.
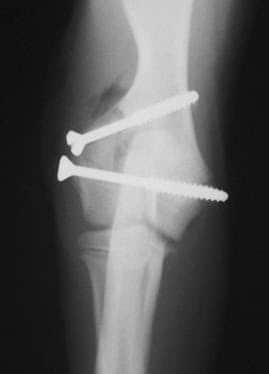
Lateral Humeral Condylar Fracture Repaired With Screws
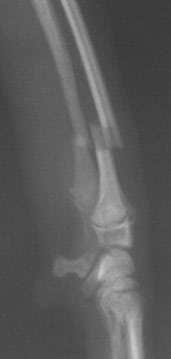
Distal Radius and Ulna Fracture
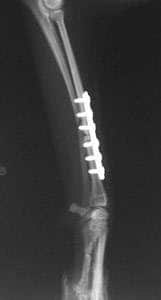
Radius and Ulna Fracture Repaired
Other Examples of Small Animal Fractures
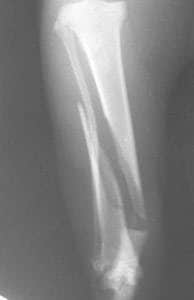
Tibial Fracture In A Cat
Severe Femoral Fracture In A Cat
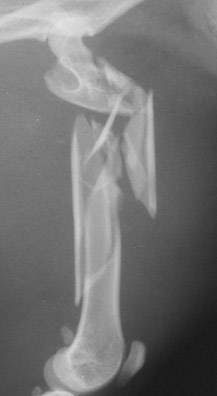
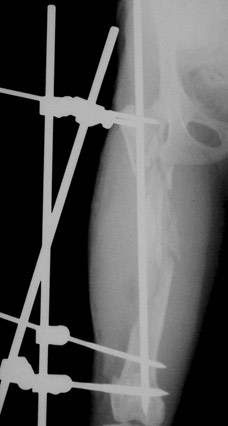
healing
Stabilization of the severe femoral fracture was done using a pin and external skeletal fixator. While restoration and fixation of all pieces was not possible, this repair technique provided stability and allowed the cat to use the leg during the healing period.